A few that will tug at your heart:
The Best Definition of Grief I’ve Ever Heard. (Ever.)
This is the Best Response I’ve ever Heard about How to Process Grief.
Rumi on Grief. There’s no Such thing as Separation.
Why we Need to Stop Saying, “I’m Sorry For Your Loss.”
What to Say (Or Not to Say) to Someone Who is Grieving:
There were about 150 people at my father’s memorial service. Standing in the receiving line afterward it seemed like every conversation, whether it was with an old friend or a total stranger, began with the exact same phrase, “I’m sorry for your loss.” Most conversations didn’t go far beyond that, partly because there’s not much to say in response except, “thank you.”
A few people managed to mix in another platitude like, “He’s in a better place now” or, “At least his suffering is over,” but it all started to sound like a broken record pretty quickly; one that I had heard many times before, seen played out in movies and even unknowingly participated in myself. Now it was being played for me at one of the most painful moments of my life, and the hollowness of that experience would literally change my course forever.
Why do so many of us struggle with what to say to someone who is grieving?
Perhaps it’s because of our cultural death phobia, and the way it pathologizes everything related to sadness. If we’re not better at dealing with grief, then it’s because we’ve never been taught better. Unfortunately, that leaves the majority of people with only one stock phrase in their repertoire, “I’m sorry for your loss.”
1. Grieving Needs More than Clichés.
One problem is simply the overwhelming use of this one phrase, while simultaneously reserving it almost exclusively for the family. It seems as the close friends aren’t really grieving at all, while family members get the idea of loss hammered into them over and over.
Saying, “I’m sorry for your loss” is a bit like the cashier saying, “Have a nice day,” at the convenience store. It betrays a lack of original thought and is so pervasive it has become irritating for many.
When responses are this programmed, how sincere is the sentiment? As more people start to become irritated by it, choosing this particular phrase because it feels “safe” isn’t really that safe anymore.
2. Clarity Works. Euphemisms Don’t.
Using the language of loss as a euphemism for death is one of many ways in which our culture conceals the reality of death, perpetuates our phobias about it, and keeps us trapped. Spoken by a griever, “I lost my mother in 2015” is being used to avoid saying the word “died.” Spoken to a griever it expresses pity combined with distancing, “I’m sorry for your loss.”
The problem is that it’s linguistically incorrect. The verb “to lose” is active, something we do. The reality of grief is that someone else died. You didn’t lose them in the same way you would lose your car keys or your wallet, and depending on your religious convictions you may not feel like you lost them at all.
For most of my life, I definitely thought of deceased loved ones as lost because I was well trained by the culture to do so. Visiting a Native American friend one day I said something about losing someone and my friend responded, “You don’t have to lose someone just because they died.”
That was the first time I was exposed to the idea that it’s possible to live in the presence of the dead, not as frightening ghosts, but as honored members of the clan.
These days I’ve become accustomed to drawing comfort from the idea that I’m living in the presence of departed loved ones. Actually, speaking to them in quiet moments when I’m alone is one of several key components—like meditation, being in nature or remembering special occasions—I use to process my grief whenever it shows up. Whether one wishes to think about that in terms of psychology or in terms of the spiritual language, it seems completely irrelevant. All I know is that I find it helpful.
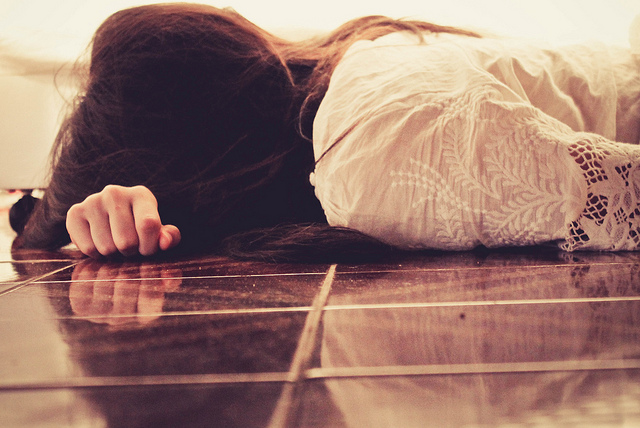

3. It’s the Wrong Mental Programming.
Experts in the field of grief care (Stephen Jenkinson, for example) are starting to recommend using the language of suffering, healing, and overcoming challenges instead. The language of loss refutes the notion that there might be an upside to grief, a spiritual deepening that can result from being exposed to something that’s an inevitable consequence of being born and choosing to love each other. By shifting to the language of suffering, healing, and overcoming challenges instead, death and grieving can once again become the redemptive processes I’ve come to believe they were always meant to be.
After personally experiencing the old cliché and its real world application thousands of times over several decades, I remember quite vividly the first time someone said, “I’m sorry for your suffering. I’m here with you.”
How different those words felt!
I immediately knew the stranger sitting next to me on a park bench somehow understood something that had been missed by all the close friends and family who had been sorry for my loss, but not present with my suffering.
Firstly, she knew I was suffering, and her use of the word “sorry” came across as authentic compassion rather than pity. Second, there was no distancing or avoidance in the way she said it. She knew what I needed most: validation of my grief and someone willing to listen, even if that meant listening through some tears. Best of all there was no judgment.
Alternative Suggestions of What to Say to People Who are Grieving
Significant numbers of people are starting to open up about their dissatisfaction with this worn out cliché. Others seem almost determined to defend it as the ultimate expression of sympathy. What the defenders don’t seem to understand is that no one will ever be offended or hurt by not saying, “I’m sorry for your loss.”
For those wanting to improve their grief communication by eliminating clichés with more accurate, helpful, and authentic responses, but still aren’t sure what to say, here are a few other choices in no particular order. These are just a few of the many options available, and they can be combined in various ways to make them both personal and appropriate.
1. I’m sorry you’re suffering right now, but I’m here with you and willing to help any way I can. Is there anything you need right now?
2. I’m sorry for whatever challenges might lie ahead for you, but I’m here and willing to help. Would it be okay if I call next week just to check in with you?
3. Please accept my deepest condolences. I can’t imagine what you must be going through right now, but I know enough about grief to know that it can be very challenging. Don’t hesitate to call me if there’s anything I can do to help.
4. I’m so sorry to hear about _____. I’m sure you’re going to miss him/her terribly. How are you holding up?
5. I know there’s nothing I can say right now to make things better, but I also know that having someone to talk to at times like this is really important, so don’t hesitate to call me whenever you need to.
Follow any of those with what you loved most about the deceased or tell a story about a favorite memory of them, and I think most people will be pleased with the deep level of connection that’s instantly created. I’m absolutely certain the bereft will feel less isolated and better supported.
One reason is that the phrases above easily open into longer conversations, while “I’m sorry for your loss” tends to shut them down. In some cases, it’s even appropriate to simply remain silent and offer them a deeply heartfelt hug instead.
Most important of all is just being willing to listen and be present.
Another one you might like:
11 Kinds of Unhelpful People You May Encounter while Grieving.
Relephant Watch:
5 Mindful Things to do Each Morning:
Author: Ed Preston
Image: Wiki Commons
Editor: Sara Kärpänen
 Share on bsky
Share on bsky





Read 191 comments and reply